- (512) 252 - 7075
- mvc1010@yahoo.com
- Mon - Thurs: 8:00 AM - 5:30 PM
29 Aug, 2022 | vwssupport | No Comments
Present Value of an Annuity Explanation & How to Determine
Fortunately, our present value annuity calculator solves these problems for you by converting all the math headaches into point and click simplicity. The Present Value of Annuity Calculator applies a time value of money formula used for measuring the current value of a stream of equal payments at the end of future periods. On the other hand, an “ordinary annuity” is more so for long-term retirement planning, as a fixed (or introduction to financial and managerial accounting variable) payment is received at the end of each month (e.g. an annuity contract with an insurance company). Having $10,000 today is better than being given $1,000 per year for the next 10 years because the sum could be invested and earn interest over that decade. At the end of the 10-year period, the $10,000 lump sum would be worth more than the sum of the annual payments, even if invested at the same interest rate.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
Many websites, including Annuity.org, offer online calculators to help you find the present value of your annuity or structured settlement payments. These calculators use a time value of money formula to measure the current worth of a stream of equal payments at the end of future periods. The future value of any annuity equals the sum of the future values for all of the annuity payments when they are moved to the end of the last payment interval. For example, assume you will make [latex]\$1,000[/latex] contributions at the end of every year for the next three years to an investment earning [latex]10\%[/latex] compounded annually.
What is your current financial priority?
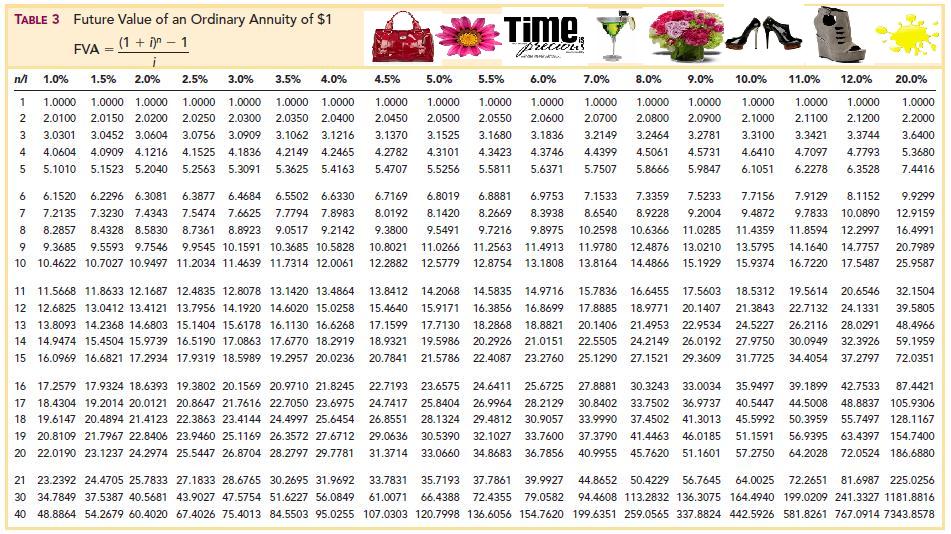
Understanding annuity tables can be a useful tool when building your retirement plan. An ordinary annuity is a series of recurring payments that are made at the end of a period, such as payments for quarterly stock dividends. An annuity due, by contrast, is a series of recurring payments that are made at the beginning of a period. So, for example, if you plan to invest a certain amount each month or year, FV will tell you how much you will accumulate as of a future date. If you are making regular payments on a loan, the FV is useful in determining the total cost of the loan.
Formula and Calculation of the Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity
People yet to retire or those that don’t need the money immediately may consider a deferred annuity. Present value (PV) is an important calculation that relies on the concept of the time value of money, whereby a dollar today is relatively more “valuable” in terms of its purchasing power than a dollar in the future. You might want to calculate the present value of the annuity, to see how much it is worth today. This is done by using an interest rate to discount the amount of the annuity.
\boxed2.2[/latex] Future Value of Ordinary Annuities
Getting early access to these funds can help you eliminate debt, make car repairs, or put a down payment on a home. The present value (PV) of an annuity is the discounted value of the bond’s future payments, adjusted by an appropriate discount rate, which is necessary because of the time value of money (TVM) concept. Although you could use this technique to solve all future value of an annuity situations, the computations become increasingly cumbersome as the number of payments increases.
What’s the Difference Between the Present Value and Future Value?
This concept helps you compare future income streams with current investment opportunities, allowing you to make informed financial decisions. In simpler terms, it tells you how much money the annuity will be worth after all the payments are received and compounded with interest. The future value tells you how much a series of regular investments will be worth at a specific point in the future, considering the interest earned over time.
Payments on mortgage loans usually require monthly payments of principal and interest. Annuity.org carefully selects partners who share a common goal of educating consumers and helping them select the most appropriate product for their unique financial and lifestyle goals. Our network of advisors will never recommend products that are not right for the consumer, nor will Annuity.org.
- Assuming that the term is 5 years and the interest rate is 7%, the present value of the annuity is $315,927.28.
- The calculator has a large LCD screen at the top which is displaying the number “0.”.
- But annuities can also be more of a general concept that describes anything that’s broken up into a series of payments.
- Suppose that Black Lighting Co. purchased a new printing press for $100,000.
Annuity tables are visual tools that help make otherwise complex mathematical formulas much easier to calculate. They lay the calculations for predetermined numbers of periodic payments against various annuity rates in a table format. You cross reference the rows and columns to find your annuity’s present value. The present value of an annuity is the current value of all future payments you will receive from the annuity. This comparison of money now and money later underscores a core tenet of finance – the time value of money.
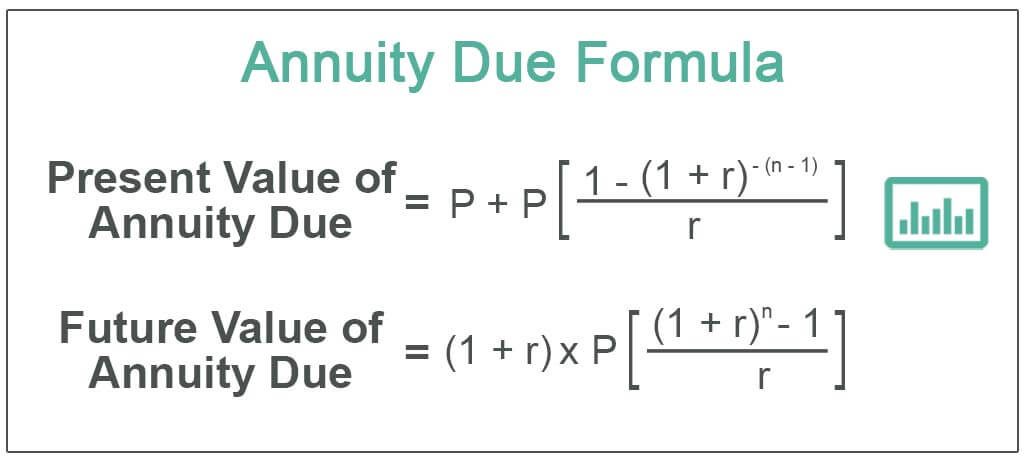
The present value of an annuity refers to the present value of a series of future promises to pay or receive an annuity at a specified interest rate. Now let’s explore annuity due, where payments happen at the beginning of each period. For instance, a $5,000 investment that yields 5% will earn more than $8,100 over the next decade. In addition to your contribution, you were able to reap more than $3,100 thanks to reinvested earnings. Studying this formula can help you understand how the present value of annuity works. For example, you’ll find that the higher the interest rate, the lower the present value because the greater the discounting.
11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. For example, suppose that a bank lends you $60,000 today, which is to be repaid in equal monthly installments over 30 years. Mortgages and certain notes payable in equal installments are examples of present-value-of-annuity problems. By calculating the present value, you can understand the effective cost in today’s dollars, potentially helping you with budgeting or financial planning. Bankrate has partnerships with issuers including, but not limited to, American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi and Discover.
Money received earlier allows it more time to earn interest, potentially leading to a higher future value compared to an ordinary annuity with the same payment amount. A dollar invested today not only earns a return over a specific period of time, but that return earns a return as well. But as an investor, you might want to understand annuity tables, especially if you’re relying on guaranteed income to fund your retirement. To account for payments occurring at the beginning of each period, the ordinary annuity FV formula above requires a slight modification.
